(January 10, 2011 – BUSINESS WIRE) — World investment in renewable energy will top $2 trillion on a cumulative basis from 2010 through 2015, driven by growth in Asia, North America, and Europe. Were the companies building these generating plants to utilize existing, commercially available nanotechnologies, ABI Research estimates, over the same five-year period renewable power producers could save nearly $300 billion in capital expenditure.
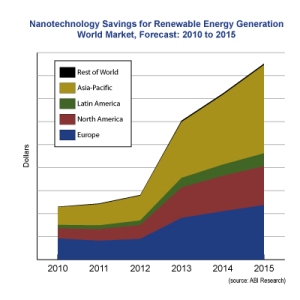
For example, says research director Larry Fisher of NextGen (ABI Research’s emerging technologies research incubator), "Incorporating nanomaterials into wind turbine blades can make them stronger, lighter and more durable, so they last longer while generating more electricity."
The Energy Information Administration (EIA) of the US Department of Energy (DOE) expects world energy consumption to grow 44% from 2008’s 283 quadrillion BTUs to 678 quadrillion BTUs (7.15 exajoules) by 2030. This increase will be driven by growing energy demand from developing nations such as China and India. Concurrently, the monetary and environmental costs of fossil fuel-based power are making it necessary for governments around the world to shift electricity production to alternative forms of energy.
Fisher observes that, "The addition of nanomaterials to manufacturing processes makes solar cells, wind turbines and fuel cells cheaper to produce, while improving their efficiency in generating electricity. These factors together make even more convincing the argument that we need to move our electrical production away from fossil fuels and increasingly toward renewable sources."
ABI Research anticipates that between 2010 and 2015, new solar photovoltaic installations and new wind installations implemented over the forecast period will total 652 gigawatts (GW) of new energy production. Fuel cell shipments will total more than 35 million units over that period as well, indicating that sector is on the cusp of global commercialization.
A new study by ABI Research, "Nanotechnologies for Green Power Generation" (http://www.abiresearch.com/research/1005396) examines how the use of nanotechnology and nanomaterials in the production of solar (photovoltaic) cells, wind turbines and blades, and fuel cells, can increase these products’ efficiency in generating electricity, as well as reducing manufacturing costs and improving durability. It is part of the firm’s Energy and Clean Technology Research Service (http://www.abiresearch.com/products/service/Energy_And_Green_Technology_Research_Service).
ABI Research provides in-depth analysis and quantitative forecasting of trends in global connectivity and other emerging technologies. For more information visit www.abiresearch.com
Follow Small Times on Twitter.com by clicking www.twitter.com/smalltimes. Or join our Facebook group

